THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is a chemical compound that is responsible for the majority of marijuana or cannabis’s psychoactive effects. According to a recent study “THC’s chemical structure is similar to the brain chemical anandamide”, which is a very interesting finding, considering that not until the last decade or so has marijuana begun to dig itself out of the stigma of being bad for you.1
We will discuss what THC is, and the effects of tetrahydrocannabinol in this article.
What is THC, or Tetrahydrocannabinol?
THC is a kind of lipid that is found in the cannabis plant and it is assumed to be actively involved in the evolutionary adaptation of plants, UV light, environmental stress, and insect predation.
Due to the similarity of THC’s chemical structure to that of Anandamide, THC can affix itself to cannabinoid receptors in a few areas of our brain that are associated with memory, thinking, perception, pleasure, and coordination.
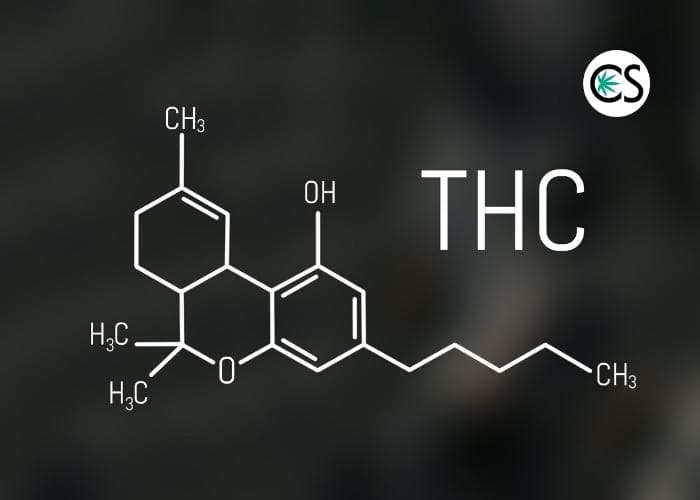
THC is a compound found in the secretion of resin by a marijuana plant’s gland. These glands are mostly found around the plant’s reproductive organs.
There are other cannabinoids that are found in the plant’s glands resin other than THC, such as CBD. CBD is by nature non-psychoactive which means it does not cause high like THC.

The Concentration of THC in Cannabis Plants
The hemp plant is a type of cannabis plant that contains a maximum of 0.3% THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol. The hemp plant is used to produce industrial hemp products like paper, rope, and hemp blocks, along with CBD products, like CBD gummies, CBD topicals, CBD capsules, and more.
The marijuana plant, also a type of cannabis plant, on the other hand, produces THC that can have a potency between 4% to 90%.
Growing techniques have increased the potency that at one time had an average of 4% potency in marijuana that someone may have smoked in the 1980s, to the high potency that we currently have in the strains of marijuana that are found in the market today.
Effects of TCH on the Body
THC or tetrahydrocannabinol stimulates brain cells to create euphoria by releasing dopamine. THC also starts to interfere with how the processing of information occurs in the brain’s hippocampus (responsible for the formation of new memories).
THC may induce hallucinations, cause delusions, or change one’s thinking process. Depending on the potency of the marijuana used in the product or flower smoked, the effects may last two hours or more.
Reported THC’s effects include anxiety, elation, short-term memory loss, tachycardia, sedation, pain relief, relaxation, etc.

Medicinal Uses of THC
Marijuana has been used for medicine-related purposes for about 3000 years or more. In 1996 California became the first state to legalize medical cannabis. While it is not currently federally legal, many states have begun to legalize the medical use of marijuana on a state level, while some have also legalized it recreationally.
THC is extracted or synthesized from cannabis to produce many THC-based products that can be found on the open market, and FDA-approved a drug called Dronabinol which is a synthetic compound that contains cannabinoids found in the marijuana. Dronabinol is used to prevent or treat vomiting and nausea associated with medications for cancer. It is also used to increase the appetite of AIDS patients.
Studies have also shown evidence that if properly used THC may assist in alleviating pain, and insomnia, along with relieving anxiety. offer additional health benefits or medical benefits.
Overdosage of THC
While it is nearly impossible to overdose in the traditional sense when consuming THC, some people do experience an “overdose” effect when consuming too much THC. This usually occurs when someone has consumed a high milligram dose of THC edibles. As legalization and the stigma surrounding THC begins to move throughout the United States, “overdosing” on THC edibles will continue to grow.
Some people, who are now becoming aware of marijuana as a substance that they feel comfortable consuming, decide that edibles are a way to dip their toe into consuming THC. While this is a great way to see if THC is for you, the issue is that many edibles are produced with high potency. The moral of the story is that if you are interested in THC edibles, please start with a low-dose edible.
THC can last longer in the gastrointestinal tract with great intensity for about 6 to 8 hours. Whereas, inhalation of THC usually lasts an hour to 3 hours.
THC vs CBD (Medical Benefits)
THC and CBD may have similar medical effects or benefits depending on the user, and product. Both may offer relief from multiple health conditions. However, THC produces a psychoactive effect, which CBD does not.
Due to this fact, some people prefer CBD to THC due to its lack of a psychoactive effect.
In the year 2018, the legal drug Epidiolex was approved by the FDA and it turned out to be the first-ever prescription drug that contained CBD. It is used in treating difficult-to-check and rare types of Epilepsy.
CBD may assist in giving you relief from:
- Inflammation
- Chronic Pain
- Seizures
- Insomnia
- Nausea
- Stomach Issues
- Migraines
- Skin issues
- Anxiety
- Depression
Whereas, THC may assist with the following:
- Muscle spasticity
- Pain
- Insomnia
- Glaucoma
- Nausea
- Anxiety
- Low appetite issues
THC vs CBD (Side Effects)
Take a deep dive into the side effects of CBD
Even in large dosages, CBD can be well tolerated. Whereas, THC can cause side effects that are temporary such as, coordination issues, imbalance, increase in heart rate, dry mouth, bloodshot eyes, slowed reaction time, anxiety, and memory loss.
Side effects of CBD include,
Fatigue, weight loss, appetite changes, diarrhea, and dizziness.
THC Drug Testing
Discover if CBD will show up on your drug test
THC cannabinoids are stored in the fat of the body. They can easily show up even after many weeks or days after consumption if tested for drugs.
Not every test can detect CBD but there are CBD-sensitive tests available. All the standard tests for a drug will check for THC chemicals thus, marijuana or THC consumption might show on a screening.
Summary
THC has medical benefits and is safe if consumed under proper guidance or dosage. You need to consider the side effects as well if you are consuming high doses of marijuana or THC. It might also interact with other drugs that you are taking on a daily basis for other health issues. Always consult with a doctor before you use any products containing THC.
references
1NIDA. 2021, April 13. How does marijuana produce its effects?. Retrieved from https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana/how-does-marijuana-produce-its-effects on 2022, June 9
2Webb, C. W., & Webb, S. M. (2014). Therapeutic benefits of cannabis: a patient survey. Hawai’i journal of medicine & public health : a journal of Asia Pacific Medicine & Public Health, 73(4), 109–111.

