What is the Endocannabinoid System?
This is a full and comprehensive guide to the endocannabinoid system (ECS). So we’ll outline how both CBD and THC communicate with the ECS to cause changes in the body.
The ECS is a complex cell-signalling system that is just as important to life as the ability to respire or to digest food. Consequently, it can have very positive effects on the body. In this article, we aim to break down the functions of the ECS in an easy-to-digest manner. We also want people to understand what the endocannabinoid system (ECS) can potentially do.
The Endocannabinoid System – What Is It and How Does It Work?
The endocannabinoid system, or ECS, is a complex communication system for the cells present in all mammals. It plays a role in regulating sleep, mood, appetite, memory and reproduction. In fact, research is beginning to show what a big part the ECS has played in the evolution of all vertebrate life on the planet. The endocannabinoid system is a network of molecules, receptors and enzymes that interact with your health and wellbeing.
How Does the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) Work?
The ECS is present in the central nervous system (CNS) of the human body. This would mainly be the brain and spinal cord. However, it also plays a role throughout almost all of the body. The ECS consists of 3 main aspects – endocannabinoid molecules, endocannabinoid receptors and metabolic enzymes.
Endocannabinoid Molecules
Cannabinoid molecules exist within your body naturally. These are endogenous cannabinoids or endocannabinoids. They are similar to the cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. However, your body naturally produces them whether you have consumed cannabis or not.
The two main endocannabinoid molecules that have been identified by scientists are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). These neurotransmitters interact with endocannabinoid receptors to cause physiological effects.
Endocannabinoid Receptors
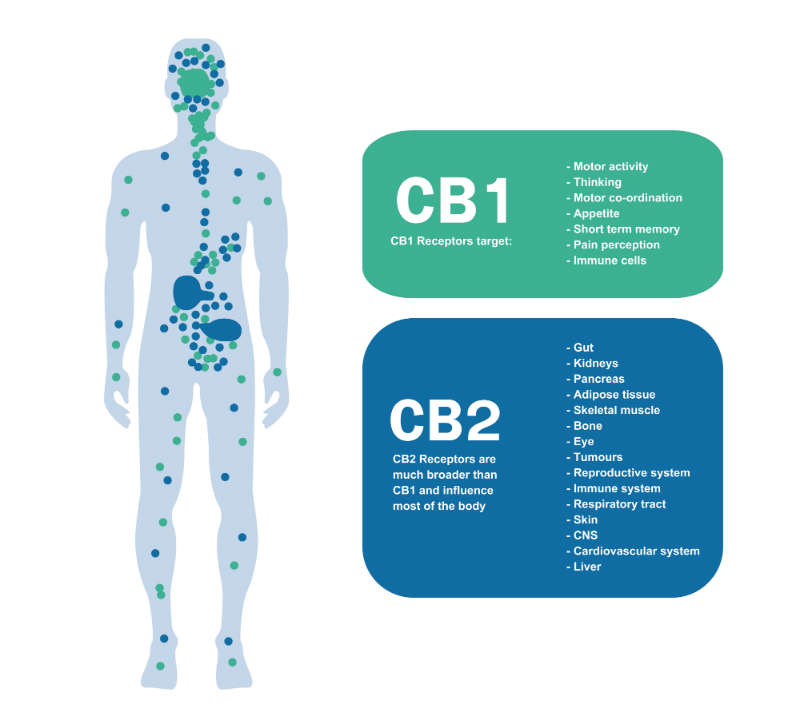
Receptors for the ECS are located throughout the body but predominantly within the nervous system. The two main types of endocannabinoid receptor are CB1 and CB2, both of which play different functions:
CB1 Receptors – Found in the central nervous system mostly in the brain and spinal cord. It’s mostly associated with cerebral effects such as behaviour, memory, cognition, motor control, appetite and pain.
CB2 Receptors – Located in the peripheral nervous system. It affects the immune system and inflammation response.
Metabolic enzymes
The responsibility of metabolic enzymes in the ECS is to break down molecules once they have carried out their function into molecules that can easily be excreted out of the body.
The ECS and Homeostasis
Research into the ECS is still in its infancy. Due to its complex nature, the exact biological pathways by which cannabinoids cause physiological effects aren’t fully understood. However, scientists believe that the endocannabinoid system’s predominant function is to maintain homeostasis within the body.
Homeostasis is defined as the tendency for a system to self-regulate to maintain an equilibrium. This results in a stable physiological effect. For example, when something within the body operates outside of a stable range, the body will respond accordingly to correct this change and bring it back into balance.
Endocannabinoid molecules respond to changes in the body. Like if the body temperature is too high for example. The idea is that the ECS creates a molecule, which will bind to a certain receptor to regulate something in the body. Such as the temperature returning back to the correct level. Once the effect has been caused, the enzymes break down the endocannabinoid molecules for excretion.
What Are the Functions of the ECS?
The ECS is located throughout the whole body. It’s responsible for a whole variety of different physiological functions. Research links the ECS with a wide range of functions. It is commonly linked with:
- The immune system and autoimmune disease
- Chronic pain conditions
- Inflammation
- Neurological and neurodegenerative disease

The Immune System
Lots of chronic illnesses are caused by immune system issues. Multiple sclerosis (MS), Crohn’s disease and type 1 diabetes to name a few. These autoimmune diseases result from a signalling issue. An immune response triggers because some cells of the body are seen as foreign invaders. The lack of recognition triggers the immune system to attack these unrecognised cells in response.
Research is currently in progress to see how exactly cannabinoids like cannabidiol interact with the ECS. Early studies have shown how promising the effects of cannabinoids could potentially be on the ECS.
Everyday Aches & Pains
Cannabinoids can be a non-opioid alleviation for everyday aches and pains. In addition to this, they come with non-addictive properties. The most common medical use for cannabinoids in the US is for common aches and pains. Some sports stars have even recommended buying and using cannabinoids to aid muscle recovery.
THC and the ECS
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the most studied and understood cannabinoid found within the cannabis plant. It’s famous for its intoxicating properties. In other words, it can get you high.
When ingested, THC can bind to both CB1 and CB2 receptors where it exerts intense effects on both the body and the mind. THC may reduce pain, stimulate your appetite, get you high and give your body a numb tingling feeling. Whilst THC is known for its intoxicating properties, it can also offer relief from the symptoms of some conditions. Consequently, it is legal in some jurisdictions for medical use.
CBD With the ECS
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the sister molecule to THC. It does not directly bind to the CB1 receptors as THC does so it does not have any intoxicating effects. In fact, CBD does not appear to directly bind to either of the main cannabinoid receptors, but instead it changes the way other cannabinoids bind, including the endocannabinoids previously mentioned.
Medical research into CBD is still in its infancy, but the initial findings and anecdotal evidence suggest that CBD could help alleviate the symptoms of a variety of conditions. This has propelled the CBD market into a multi-billion dollar industry over recent years.
Endocannabinoid Deficiency
More people are researching the way cannabinoids (and endocannabinoids) affect different people in different ways. Theories have begun to emerge linking autoimmune, inflammatory and neurological conditions to a deficiency in some endocannabinoids.
Key Conclusions
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) has an extremely important biological role in human life. It plays a huge part in keeping the processes of the body stable. Experts continue to develop their understanding of the ECS. As a result, we are seeing more openness towards using cannabinoids like THC and CBD to help alleviate the symptoms of some conditions.
The post The Endocannabinoid System – Everything You May Not Know About It first appeared on CBD Village UK.
